Layout Management
UI layout is a core part of building user interfaces, determining the position and size of each control on the screen. DejaOS offers several layout methods to meet various development needs. This chapter will detail absolute, relative, and Flex layouts to help you build beautiful and functional UIs flexibly and efficiently.
Absolute Layout
This is the most basic layout method. Our previous examples all used absolute layout, setting the absolute position and size of controls using setPos and setSize. Absolute layout is sufficient for most situations. Compared to mobile apps, our applications rarely need to support cross-platform, cross-device, and cross-screen scenarios. Additionally, our UI is generally less complex than that of mobile apps. Lastly, absolute layout is the most efficient method; too many relative layouts can degrade display performance on low-spec devices.
Relative Layout
Relative layout mainly relies on the align and alignTo functions. The difference is that align positions an object relative to its parent, while alignTo positions it relative to another specified object. Refer to the following enumeration for alignment options:
utils.ALIGN = {
// Position relative to the reference object. Those with OUT are outside the reference object's boundary.
OUT_TOP_LEFT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_TOP_LEFT,
OUT_TOP_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_TOP_MID,
OUT_TOP_RIGHT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_TOP_RIGHT,
OUT_BOTTOM_LEFT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_BOTTOM_LEFT,
OUT_BOTTOM_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_BOTTOM_MID,
OUT_BOTTOM_RIGHT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_BOTTOM_RIGHT,
OUT_LEFT_TOP: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_LEFT_TOP,
OUT_LEFT_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_LEFT_MID,
OUT_LEFT_BOTTOM: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_LEFT_BOTTOM,
OUT_RIGHT_TOP: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_RIGHT_TOP,
OUT_RIGHT_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_RIGHT_MID,
OUT_RIGHT_BOTTOM: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_OUT_RIGHT_BOTTOM,
TOP_LEFT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_TOP_LEFT,
TOP_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_TOP_MID,
TOP_RIGHT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_TOP_RIGHT,
BOTTOM_LEFT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_BOTTOM_LEFT,
BOTTOM_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_BOTTOM_MID,
BOTTOM_RIGHT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_BOTTOM_RIGHT,
LEFT_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_LEFT_MID,
RIGHT_MID: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_RIGHT_MID,
CENTER: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_CENTER,
DEFAULT: utils.ENUM.LV_ALIGN_DEFAULT,
};
Let's look at an example:
import dxui from "../dxmodules/dxUi.js";
import std from "../dxmodules/dxStd.js";
import logger from "../dxmodules/dxLogger.js";
dxui.init({ orientation: 1 });
const page1 = dxui.View.build("page1", dxui.Utils.LAYER.MAIN);
const button1 = dxui.Button.build("page1button", page1);
button1.align(dxui.Utils.ALIGN.CENTER, 0, 0);
button1.setSize(200, 200);
// All alignment enums
const aligns = {
OUT_TOP_LEFT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_TOP_LEFT,
OUT_TOP_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_TOP_MID,
OUT_TOP_RIGHT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_TOP_RIGHT,
OUT_BOTTOM_LEFT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_BOTTOM_LEFT,
OUT_BOTTOM_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_BOTTOM_MID,
OUT_BOTTOM_RIGHT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_BOTTOM_RIGHT,
OUT_LEFT_TOP: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_LEFT_TOP,
OUT_LEFT_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_LEFT_MID,
OUT_LEFT_BOTTOM: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_LEFT_BOTTOM,
OUT_RIGHT_TOP: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_RIGHT_TOP,
OUT_RIGHT_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_RIGHT_MID,
OUT_RIGHT_BOTTOM: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_RIGHT_BOTTOM,
TOP_LEFT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.TOP_LEFT,
TOP_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.TOP_MID,
TOP_RIGHT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.TOP_RIGHT,
BOTTOM_LEFT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.BOTTOM_LEFT,
BOTTOM_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.BOTTOM_MID,
BOTTOM_RIGHT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.BOTTOM_RIGHT,
LEFT_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.LEFT_MID,
RIGHT_MID: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.RIGHT_MID,
CENTER: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.CENTER,
DEFAULT: dxui.Utils.ALIGN.DEFAULT,
};
// Convert name to acronym, e.g., OUT_RIGHT_TOP → ORT
function getShortName(name) {
return name
.split("_")
.map((word) => word[0])
.join("");
}
// Create labels and arrange them around button1
let idx = 0;
for (const [name, align] of Object.entries(aligns)) {
const label = dxui.Label.build(`label_${idx++}`, page1);
label.text(getShortName(name));
// Place "OUT_" ones outside, others inside or on the edge
label.alignTo(button1, align, 0, 0);
}
dxui.loadMain(page1);
std.setInterval(() => {
dxui.handler();
}, 10);
Result
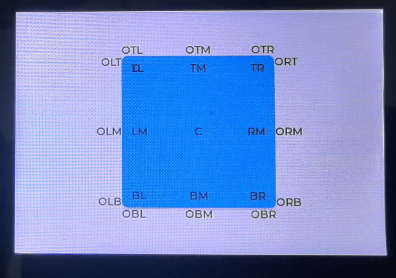
Code Analysis
This example demonstrates relative layout. For instance, the button is centered relative to page1 using align(dxui.Utils.ALIGN.CENTER, 0, 0), placing it in the exact center of the screen. If we used absolute layout here, we would need to carefully calculate the screen and button sizes to achieve perfect centering. The remaining 18 Labels are arranged around the button, visually demonstrating the 18 different relative layout positions.
Flex Layout
This is similar to the web's flexbox layout. It uses the flexFlow and flexAlign functions, with the following enumerations:
utils.FLEX_ALIGN = {
// Flex layout alignment
START: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_START,
END: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_END,
CENTER: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_CENTER,
SPACE_EVENLY: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_SPACE_EVENLY,
SPACE_AROUND: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_SPACE_AROUND,
SPACE_BETWEEN: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_ALIGN_SPACE_BETWEEN,
};
utils.FLEX_FLOW = {
// Flex layout main and cross axes
ROW: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_ROW,
COLUMN: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_COLUMN,
ROW_WRAP: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_ROW_WRAP,
ROW_REVERSE: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_ROW_REVERSE,
ROW_WRAP_REVERSE: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_ROW_WRAP_REVERSE,
COLUMN_WRAP: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_COLUMN_WRAP,
COLUMN_REVERSE: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_COLUMN_REVERSE,
COLUMN_WRAP_REVERSE: utils.ENUM.LV_FLEX_FLOW_COLUMN_WRAP_REVERSE,
};
Let's look at an example:
import dxui from "../dxmodules/dxUi.js";
import std from "../dxmodules/dxStd.js";
import logger from "../dxmodules/dxLogger.js";
dxui.init({ orientation: 1 });
const page = dxui.View.build("page", dxui.Utils.LAYER.MAIN);
/**
* Example 1: Horizontal arrangement + wrapping + center alignment
*/
const flexRow = dxui.View.build("flexRow", page);
flexRow.setSize(200, 320);
flexRow.setPos(220, 20);
// Set main axis: horizontal arrangement + wrapping
flexRow.flexFlow(dxui.Utils.FLEX_FLOW.ROW_WRAP);
// Set main axis, cross axis, and overall alignment to center
flexRow.flexAlign(
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER, // Main axis alignment (horizontal)
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER, // Cross axis alignment (vertical)
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER // Overall container alignment
);
// Add some child items
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
const item = dxui.Label.build(`row_item_${i}`, flexRow);
item.text(`R${i}`);
item.setSize(60, 40);
item.bgColor(0x99ccff);
item.radius(6);
item.padAll(4);
}
/**
* Example 2: Vertical arrangement + space-evenly distribution
*/
const flexCol = dxui.View.build("flexCol", page);
flexCol.setSize(200, 400);
flexCol.align(dxui.Utils.ALIGN.OUT_BOTTOM_MID, 0, 20);
// Set main axis: vertical arrangement
flexCol.flexFlow(dxui.Utils.FLEX_FLOW.COLUMN);
// Alignment: space-evenly on main axis, center on cross axis
flexCol.flexAlign(
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.SPACE_EVENLY, // Main axis: evenly distributed vertically
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER, // Cross axis: centered horizontally
dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER
);
// Add child items
["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"].forEach((ch, i) => {
const lbl = dxui.Label.build(`col_item_${i}`, flexCol);
lbl.text(`C${ch}`);
lbl.setSize(100, 40);
lbl.bgColor(0xffcc99);
lbl.radius(6);
lbl.padAll(4);
});
dxui.loadMain(page);
std.setInterval(() => {
dxui.handler();
}, 10);
Result
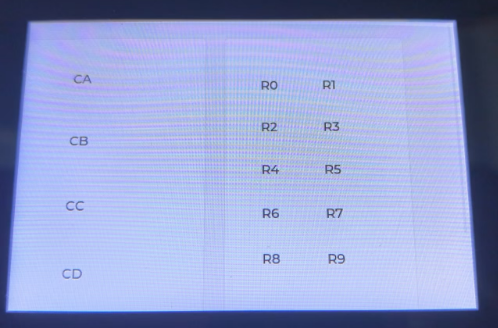
Code Analysis
This code demonstrates two common scenarios for Flex layout: horizontal wrapping and vertical even distribution.
-
Example 1: Horizontal Arrangement (
flexRow)- We create a
200x320container calledflexRow. flexRow.flexFlow(dxui.Utils.FLEX_FLOW.ROW_WRAP)sets the main axis to horizontal (ROW) and allows items to wrap (WRAP).flexRow.flexAlign(...)sets the main axis, cross axis, and overall alignment to center (CENTER), keeping the items centered both horizontally and vertically.- A loop creates 10
Labelitems (R0-R9), which are automatically arranged from left to right within the container, wrapping to the next line when there isn't enough space.
- We create a
-
Example 2: Vertical Arrangement (
flexCol)- We create a
200x400container calledflexCol. flexCol.flexFlow(dxui.Utils.FLEX_FLOW.COLUMN)sets the main axis to vertical (COLUMN).flexCol.flexAlign(dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.SPACE_EVENLY, dxui.Utils.FLEX_ALIGN.CENTER, ...)sets the main axis (vertical) alignment toSPACE_EVENLY, which means the items are distributed evenly vertically with equal space between them. The cross axis (horizontal) alignment isCENTER, centering the items horizontally within the container.- It creates 5
Labelitems (CA-CE), which are arranged vertically from top to bottom with equal spacing.
- We create a
Flex layout is ideal for scenarios that require dynamic and adaptive positioning of child items, enabling complex layouts with less and cleaner code.